Are you suffering from chronic jaw pain, headaches, or difficulty in opening and closing your mouth? If so, you may be one of the millions of people affected by temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorder. TMJ disorder is a condition that affects the joints and muscles of the jaw, causing a range of uncomfortable symptoms.
In this comprehensive guide, we will demystify the world of TMJ disorder surgery. Whether you are considering surgery as a treatment option or simply want to learn more about the procedure, this article will provide you with all the information you need.
From understanding the causes and symptoms of TMJ disorder to exploring the various surgical treatment options available, this guide will leave no stone unturned. We will answer all your questions, debunk myths surrounding TMJ disorder surgery, and provide you with the knowledge and insights to make informed decisions about your health.
Join us as we unlock the mystery of TMJ disorder surgery and empower you to take control of your health and well-being.
What is TMJ disorder?
TMJ disorder, also known as temporomandibular joint disorder, is a condition that affects the joints and muscles of the jaw. The temporomandibular joint is the joint that connects your jawbone to your skull, allowing you to open and close your mouth, chew, and speak. When this joint becomes damaged or inflamed, it can lead to a range of painful symptoms.
The exact cause of TMJ disorder is often difficult to determine, as it can be a result of various factors. Some common causes include jaw injuries, teeth grinding, arthritis, misaligned bite, stress, and even hormonal changes. The symptoms of TMJ disorder can vary from person to person, but commonly include jaw pain, headaches, earaches, clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth, and difficulty in opening and closing the mouth.
Diagnosing TMJ disorder can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. However, your dentist or oral surgeon can perform a thorough examination, which may include a physical examination of your jaw, dental X-rays, and in some cases, an MRI or CT scan to get a detailed view of the jaw joint.
Symptoms and causes of TMJ disorder
TMJ disorder can manifest in a variety of ways, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
1. Jaw pain: Individuals with TMJ disorder often experience pain in or around the jaw joint. This pain can be sharp or dull and may worsen when chewing or speaking.
2. Headaches: TMJ disorder can cause headaches, particularly in the temples or behind the eyes. These headaches can be persistent and may worsen throughout the day.
3. Difficulty opening and closing the mouth: Individuals with TMJ disorder may have trouble fully opening or closing their mouths. This limitation in jaw movement can be uncomfortable and may affect the ability to eat or speak properly.
The causes of TMJ disorder are multifactorial and can vary from person to person. Some common causes include:
1. Teeth grinding: Grinding or clenching the teeth, often done unconsciously during sleep, can put excessive pressure on the jaw joint and lead to TMJ disorder.
2. Jaw injury: Trauma to the jaw, such as a sports injury or car accident, can damage the joint and trigger TMJ disorder symptoms.
3. Arthritis: Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can affect the jaw joint and contribute to TMJ disorder.
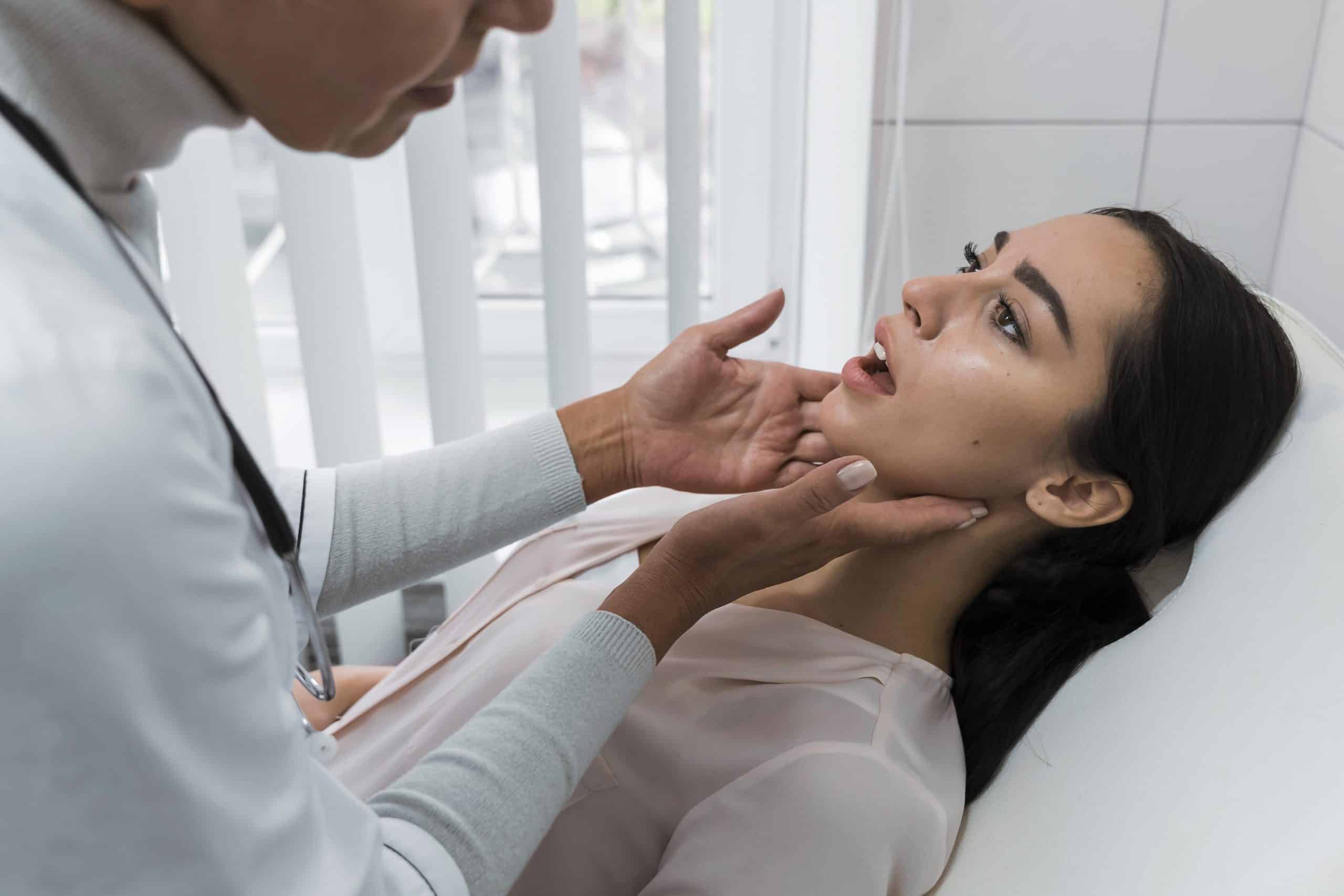
Diagnosing TMJ disorder
Diagnosing TMJ disorder involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, typically a dentist or an oral and maxillofacial surgeon. The diagnostic process may include the following steps:
1. Medical history and physical examination: Your healthcare provider will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination of your jaw, face, and neck. They will look for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and abnormalities in jaw movement.
2. Imaging tests: To obtain a detailed view of the jaw joint, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These tests can help identify any structural abnormalities or damage to the joint.
3. Bite analysis: Your dentist may perform a bite analysis to assess how your upper and lower teeth fit together. An improper bite or misalignment of the teeth can contribute to TMJ disorder.
Once a diagnosis of TMJ disorder is confirmed, your healthcare provider will discuss the available treatment options with you. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and improve jaw function.
Non-surgical treatments for TMJ disorder
In many cases, TMJ disorder can be managed without the need for surgery. Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of defense in alleviating the symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with TMJ disorder.
One of the most common non-surgical treatments for TMJ disorder is lifestyle modifications. This may include avoiding hard or chewy foods, practicing stress-reducing techniques, and using over-the-counter pain medications to manage pain and inflammation. Your dentist may also recommend physical therapy exercises to strengthen the jaw muscles and improve jaw mobility.
Another non-surgical treatment option is the use of oral appliances, such as splints or mouthguards. These devices are custom-made to fit your mouth and help alleviate the symptoms of TMJ disorder by reducing jaw clenching and grinding, improving jaw alignment, and providing cushioning for the joint.
Other non-surgical treatment options may include hot and cold therapy, massage, chiropractic adjustments, and acupuncture. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of non-surgical treatments can vary from person to person, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Therefore, it’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to find the treatment plan that is best suited to your specific needs.
Surgical treatment options for TMJ disorder
Surgery is generally considered a last resort for treating TMJ disorder when conservative measures have failed to provide relief. There are several surgical treatment options available, and the choice of procedure depends on the individual’s specific condition and symptoms. Some common surgical interventions for TMJ disorder include:
1. Arthrocentesis: This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of needles into the joint space to irrigate and flush out inflammatory byproducts. Arthrocentesis can help reduce pain and improve jaw mobility.
2. Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses small incisions and a tiny camera to visualize and treat the joint. It allows the surgeon to remove damaged tissue, repair the joint, or perform other necessary interventions.
3. Open joint surgery: In severe cases of TMJ disorder, open joint surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves making a larger incision to access the joint directly. It allows for more extensive repairs, such as joint replacement or restructuring.

Recovery and aftercare for TMJ disorder surgery
The recovery process after TMJ disorder surgery varies depending on the type of procedure performed. However, there are some general guidelines that can help promote healing and ensure a successful recovery:
1. Follow post-operative instructions: It is crucial to carefully follow the post-operative instructions provided by your surgeon. These instructions may include dietary restrictions, pain management techniques, and proper wound care.
2. Attend follow-up appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon are essential for monitoring your progress and addressing any concerns or complications that may arise.
3. Physical therapy: Physical therapy is often recommended after TMJ disorder surgery to improve jaw mobility, strengthen the muscles around the joint, and prevent future complications.
4. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to a smoother recovery. This includes eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting enough rest, and avoiding habits that can exacerbate TMJ disorder symptoms, such as teeth grinding or excessive jaw movements.
In conclusion, TMJ disorder surgery can provide relief for individuals suffering from chronic jaw pain and other associated symptoms. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available surgical treatment options is essential for making informed decisions about your health. If you are experiencing persistent jaw pain or have been diagnosed with TMJ disorder, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action. Remember, knowledge is power, and by unlocking the mystery of TMJ disorder surgery, you can take control of your health and well-being.
When is TMJ disorder surgery necessary?
While non-surgical treatments are often effective in managing TMJ disorder, there are cases where surgery may be necessary. Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief or when the condition is severe and significantly impacting the patient’s quality of life.
Before recommending surgery, your oral surgeon will thoroughly evaluate your condition and consider various factors, such as the severity of your symptoms, the underlying cause of your TMJ disorder, and the potential risks and benefits of surgery. They will also take into account your overall health and any pre-existing medical conditions that may affect your ability to undergo surgery.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about the outcomes of TMJ disorder surgery. While surgery can provide significant relief for some individuals, it may not completely eliminate all symptoms. Therefore, it’s crucial to have open and honest discussions with your healthcare provider to understand the potential benefits and limitations of surgery in your specific case.
Types of TMJ disorder surgery
There are several different types of TMJ disorder surgery, and the specific procedure recommended for you will depend on the underlying cause and severity of your condition. Some common types of TMJ disorder surgery include:
1. Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments into the joint space to remove any damaged tissue or repair the joint.
2. Arthroplasty: This procedure involves removing and replacing the damaged joint with an artificial implant. It is typically reserved for severe cases of TMJ disorder.
3. Total joint replacement: In rare cases where the joint is severely damaged and other treatment options have failed, a total joint replacement may be recommended. This involves removing the entire joint and replacing it with an artificial joint.
4. Orthognathic surgery: In some cases, TMJ disorder may be caused by a misaligned bite or jaw. Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery, can help correct the alignment of the jaw and alleviate TMJ disorder symptoms.
Each type of surgery has its own risks and potential complications, which your oral surgeon will discuss with you in detail before recommending a specific procedure. It’s important to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and make an informed decision in collaboration with your healthcare provider.
Risks and complications of TMJ disorder surgery
Like any surgical procedure, TMJ disorder surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. Some common risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, scarring, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Your oral surgeon will discuss these risks with you and take steps to minimize them.
Recovery and aftercare for TMJ disorder surgery
The recovery process after TMJ disorder surgery can vary depending on the type and extent of the procedure. In general, it’s important to follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions carefully to ensure a smooth recovery. This may include:
– Eating a soft or liquid diet for a certain period of time
– Avoiding strenuous activities and excessive jaw movement
– Taking prescribed pain medications as directed
– Attending follow-up appointments with your oral surgeon
It’s important to note that the recovery process can take several weeks or even months, and it’s normal to experience some swelling, discomfort, and limited jaw movement during this time. Your oral surgeon will provide you with specific guidelines and recommendations tailored to your individual case.
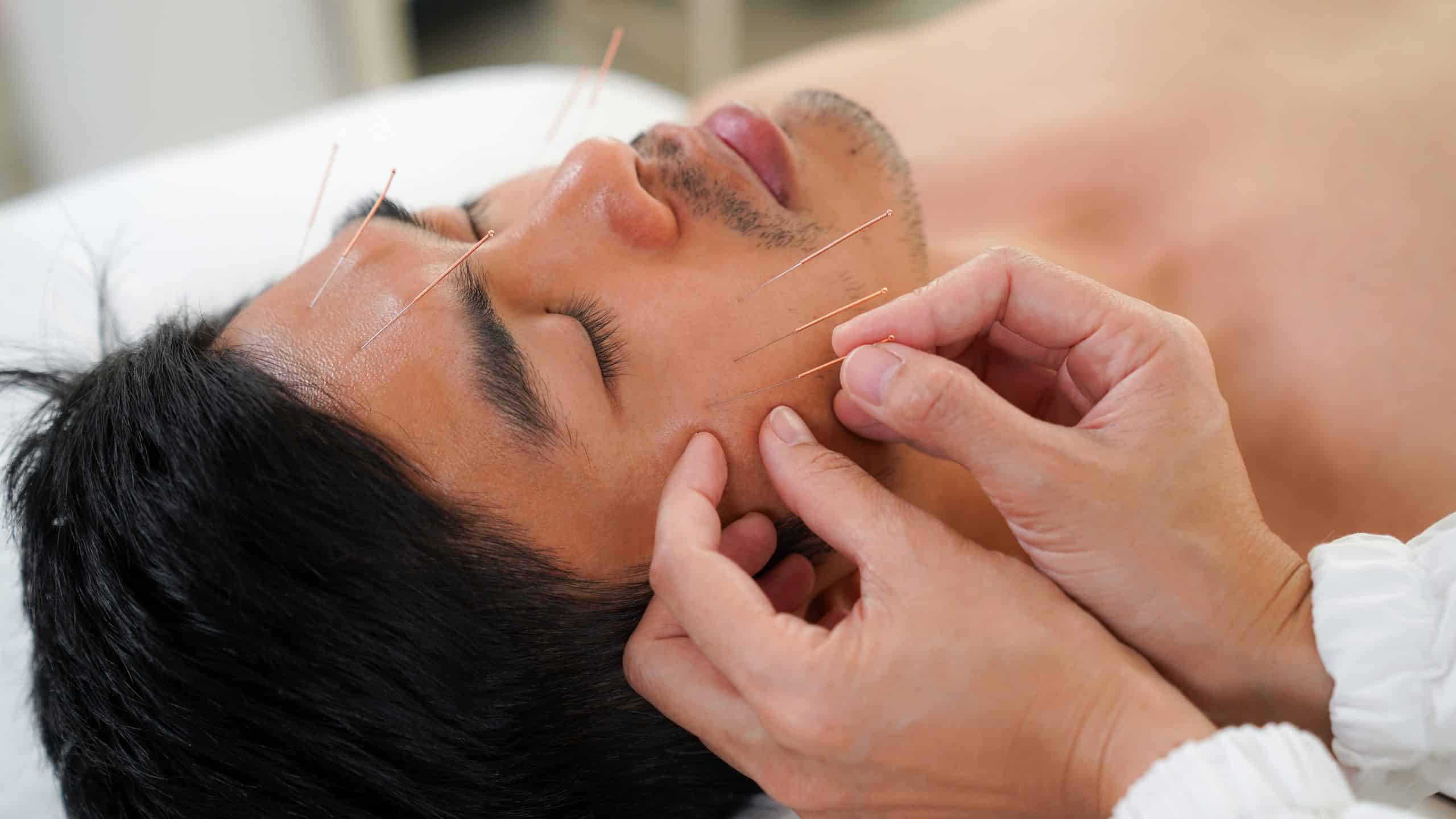
Alternative treatments for TMJ disorder
In addition to surgical and non-surgical treatments, there are also alternative therapies that some individuals find helpful in managing their TMJ disorder symptoms. These alternative treatments may include:
– Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to help alleviate pain and promote overall well-being.
– Herbal remedies: Some individuals find relief from TMJ disorder symptoms by using herbal supplements or topical creams that contain ingredients known for their anti-inflammatory properties, such as turmeric or arnica.
– Mind-body techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which may in turn alleviate TMJ disorder symptoms.
While alternative treatments may provide some relief for certain individuals, it’s important to approach them with caution and discuss them with your healthcare provider. It’s always best to use alternative treatments as complementary to, rather than a replacement for, evidence-based medical care.
Conclusion
TMJ disorder can be a challenging condition to live with, but there are treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve your quality of life. While surgery is not always necessary, it can provide significant relief for those who have exhausted non-surgical options or have severe cases of TMJ disorder.
If you are considering TMJ disorder surgery, it’s important to consult with a qualified oral surgeon who can evaluate your condition and discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgery. Remember to ask questions, communicate openly with your healthcare provider, and make an informed decision based on your individual needs and circumstances.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for TMJ disorder, you can take control of your health and well-being. Whether you choose non-surgical treatments, TMJ disorder surgery, or alternative therapies, the most important thing is to find a treatment plan that works for you and helps you live a pain-free life.