When it comes to the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery, there are several specialized areas that patients may not be familiar with. Two of these areas are oral and maxillofacial surgeons and orthognathic surgeons. While both professionals work within the realm of facial surgery, there are distinct differences between the two. Understanding these differences can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options. In this article, we will explore the unique roles of oral and maxillofacial surgeons and orthognathic surgeons, their areas of expertise, and the types of procedures they perform. By gaining a clear understanding of the distinctions between these two specialties, patients can ensure they receive the most appropriate and effective care for their specific needs. So let’s dive in and shed light on the world of oral and maxillofacial surgery and orthognathic surgery.
Education and Training Required for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are dental specialists who have completed extensive education and training beyond dental school. They undergo four to six years of surgical residency, which includes both medical and dental training. During this residency, they gain comprehensive knowledge in areas such as anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. They also develop expertise in performing a wide range of surgeries, including wisdom tooth extraction, dental implant placement, and corrective jaw surgery.
To become an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, one must first complete a Bachelor’s degree followed by four years of dental school. After obtaining their Doctor of Dental Surgery (DDS) or Doctor of Dental Medicine (DMD) degree, they must then complete a residency program accredited by the American Dental Association (ADA). This residency program is typically four to six years in duration and provides surgeons with hands-on training in a hospital setting.
Once the residency is completed, oral and maxillofacial surgeons may choose to pursue further specialization through fellowships or additional training programs. These additional training opportunities allow surgeons to gain expertise in specific areas such as facial trauma, cleft lip and palate repair, or cosmetic facial surgery. By continuously updating their knowledge and skills, oral and maxillofacial surgeons ensure that they are at the forefront of their field and capable of providing the highest level of care to their patients.
Education and Training Required for Orthognathic Surgeons
Orthognathic surgeons, on the other hand, are a subset of oral and maxillofacial surgeons who focus specifically on corrective jaw surgery. While they undergo the same education and training as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, they have chosen to specialize in the field of orthognathic surgery. This specialization allows them to develop a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between the jaws and the facial skeleton.
To become an orthognathic surgeon, one must first complete the same educational path as an oral and maxillofacial surgeon, which includes a Bachelor’s degree, four years of dental school, and a residency program accredited by the ADA. However, during their residency, orthognathic surgeons receive additional training and experience in the diagnosis and treatment of jaw deformities.
This specialized training equips orthognathic surgeons with the knowledge and skills necessary to correct various jaw abnormalities, such as overbites, underbites, and crossbites. They have a deep understanding of how the jaws should function together for optimal oral health and facial aesthetics. By focusing exclusively on orthognathic surgery, these surgeons are able to provide highly specialized care to patients who require corrective jaw procedures.
Scope of Practice for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons have a broad scope of practice that encompasses both surgical and non-surgical treatments for conditions affecting the mouth, jaws, and facial structures. They are trained to diagnose and treat a wide range of oral and maxillofacial conditions, including tooth extractions, dental implant placement, facial trauma, oral pathology, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
One of the key areas of expertise for oral and maxillofacial surgeons is the removal of impacted wisdom teeth. Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, often do not have enough space to fully emerge or develop properly. This can lead to a range of issues, including pain, infection, and damage to adjacent teeth. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are highly skilled in safely and effectively removing impacted wisdom teeth, relieving patients of discomfort and preventing further complications.
In addition to wisdom tooth extraction, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are also proficient in placing dental implants. Dental implants are a popular and durable solution for replacing missing teeth. The surgical placement of dental implants requires a high level of precision and expertise to ensure optimal results. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons have the necessary training and experience to perform this procedure with excellent outcomes.
Scope of Practice for Orthognathic Surgeons
Orthognathic surgeons focus specifically on the diagnosis and treatment of jaw deformities. They are experts in correcting discrepancies in the size, shape, or position of the jaws to improve both function and aesthetics. Orthognathic surgery is often recommended for patients with severe malocclusions or facial asymmetry that cannot be corrected with orthodontic treatment alone.
One common condition treated by orthognathic surgeons is a protruding or receding jaw. This occurs when the upper or lower jaw is positioned too far forward or backward, resulting in an imbalanced facial profile. Orthognathic surgery can effectively reposition the jaws to achieve a more harmonious facial structure and enhance the patient’s overall appearance.
Orthognathic surgeons also specialize in correcting bite problems, such as overbites, underbites, and crossbites. These misalignments can cause difficulties with chewing, speaking, and even breathing. By using advanced surgical techniques, orthognathic surgeons can bring the upper and lower jaws into proper alignment, improving both function and aesthetics.
Procedures Performed by Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
As mentioned earlier, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are trained to perform a wide range of procedures. In addition to wisdom tooth extraction and dental implant placement, they also provide treatment for facial trauma. This may include repairing fractures of the facial bones, such as the jaw, cheekbones, or eye sockets. Facial trauma can result from accidents, sports injuries, or other traumatic events, and requires immediate attention to restore function and appearance.
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are also skilled in the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial pathology. This involves the identification and management of various diseases and abnormalities affecting the mouth, jaws, and surrounding structures. Examples of oral and maxillofacial pathology include oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, and cysts or tumors of the jawbones. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons work closely with other medical professionals, such as oncologists and radiologists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with these conditions.
Procedures Performed by Orthognathic Surgeons
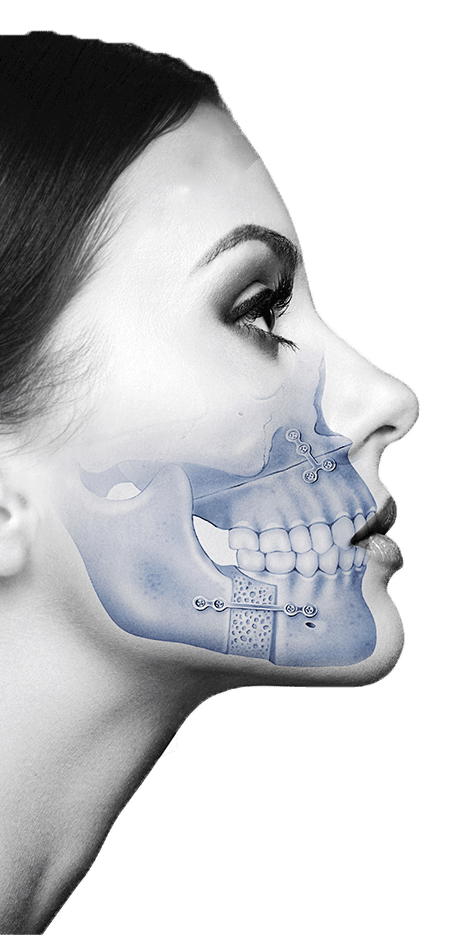
Orthognathic surgeons specialize in corrective jaw surgery, which involves repositioning the jaws to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic results. This procedure is typically performed in collaboration with orthodontists, who focus on aligning the teeth. Orthognathic surgery may be recommended for a variety of reasons, including severe malocclusions, facial asymmetry, and breathing difficulties.
During orthognathic surgery, the surgeon carefully cuts and repositions the jawbones to improve the overall bite and facial balance. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting, and the recovery period can vary depending on the complexity of the case. Orthognathic surgeons work closely with orthodontists to ensure that the teeth and jaws function together harmoniously, resulting in a well-aligned bite and an improved facial appearance.
When to See an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
Patients should consider seeing an oral and maxillofacial surgeon for a variety of reasons. If they are experiencing pain or discomfort related to their wisdom teeth, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon can evaluate the situation and recommend the appropriate treatment, which may include extraction. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons also specialize in dental implant placement, making them the ideal choice for patients considering this tooth replacement option.
Furthermore, if a patient has suffered facial trauma, such as a fractured jaw or cheekbone, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon can provide immediate care to repair the damage and restore normal function. Additionally, if a patient has been diagnosed with an oral or maxillofacial pathology, such as oral cancer or a jaw cyst, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon can develop an appropriate treatment plan and coordinate care with other specialists as needed.
When to See an Orthognathic Surgeon
Patients should consider seeing an orthognathic surgeon if they have significant jaw abnormalities that are affecting their bite, facial aesthetics, or overall quality of life. Orthognathic surgery may be recommended when orthodontic treatment alone cannot correct these issues. If a patient has a severe overbite or underbite, crossbite, or facial asymmetry that is causing functional problems or impacting their self-esteem, an orthognathic surgeon can assess the situation and determine if surgical intervention is necessary.
It is important to note that orthognathic surgery is typically performed after completion of orthodontic treatment. This is because the teeth must be properly aligned before the surgical repositioning of the jaws can take place. Orthodontists and orthognathic surgeons work together to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the alignment of the teeth and the position of the jaws, resulting in a well-balanced and functional bite.
Choosing Between an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon and an Orthognathic Surgeon
Choosing between an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and an orthognathic surgeon depends on the specific needs of the patient. If the patient requires treatment for conditions such as impacted wisdom teeth, dental implant placement, facial trauma, or oral and maxillofacial pathology, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon is the appropriate choice. These surgeons have the expertise to address a wide range of oral and facial conditions and provide comprehensive care.
On the other hand, if the patient has significant jaw abnormalities that are affecting their bite, facial aesthetics, or overall quality of life, an orthognathic surgeon may be the best option. Orthognathic surgeons specialize in corrective jaw surgery and have the knowledge and skills necessary to reposition the jaws and improve both function and appearance.
It is important for patients to consult with both oral and maxillofacial surgeons and orthognathic surgeons to determine the most appropriate course of treatment. These specialists will evaluate the patient’s specific needs and develop a customized treatment plan that addresses their unique concerns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, oral and maxillofacial surgeons and orthognathic surgeons play distinct roles within the field of facial surgery. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons have a broad scope of practice that includes the diagnosis and treatment of a wide range of conditions affecting the mouth, jaws, and facial structures. They are skilled in performing procedures such as wisdom tooth extraction, dental implant placement, and facial trauma repair.
Orthognathic surgeons, on the other hand, specialize in corrective jaw surgery and focus specifically on repositioning the jaws to improve both function and aesthetics. They are experts in treating severe malocclusions, facial asymmetry, and bite problems that cannot be corrected with orthodontic treatment alone.
By understanding the differences between these two specialties, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options and ensure they receive the most appropriate and effective care for their specific needs. Whether it’s an oral and maxillofacial surgeon or an orthognathic surgeon, patients can trust in the expertise of these highly trained professionals to provide the highest level of care and achieve optimal outcomes.